Hi, message us with any questions.
We're happy to help!

🌍 Introduction
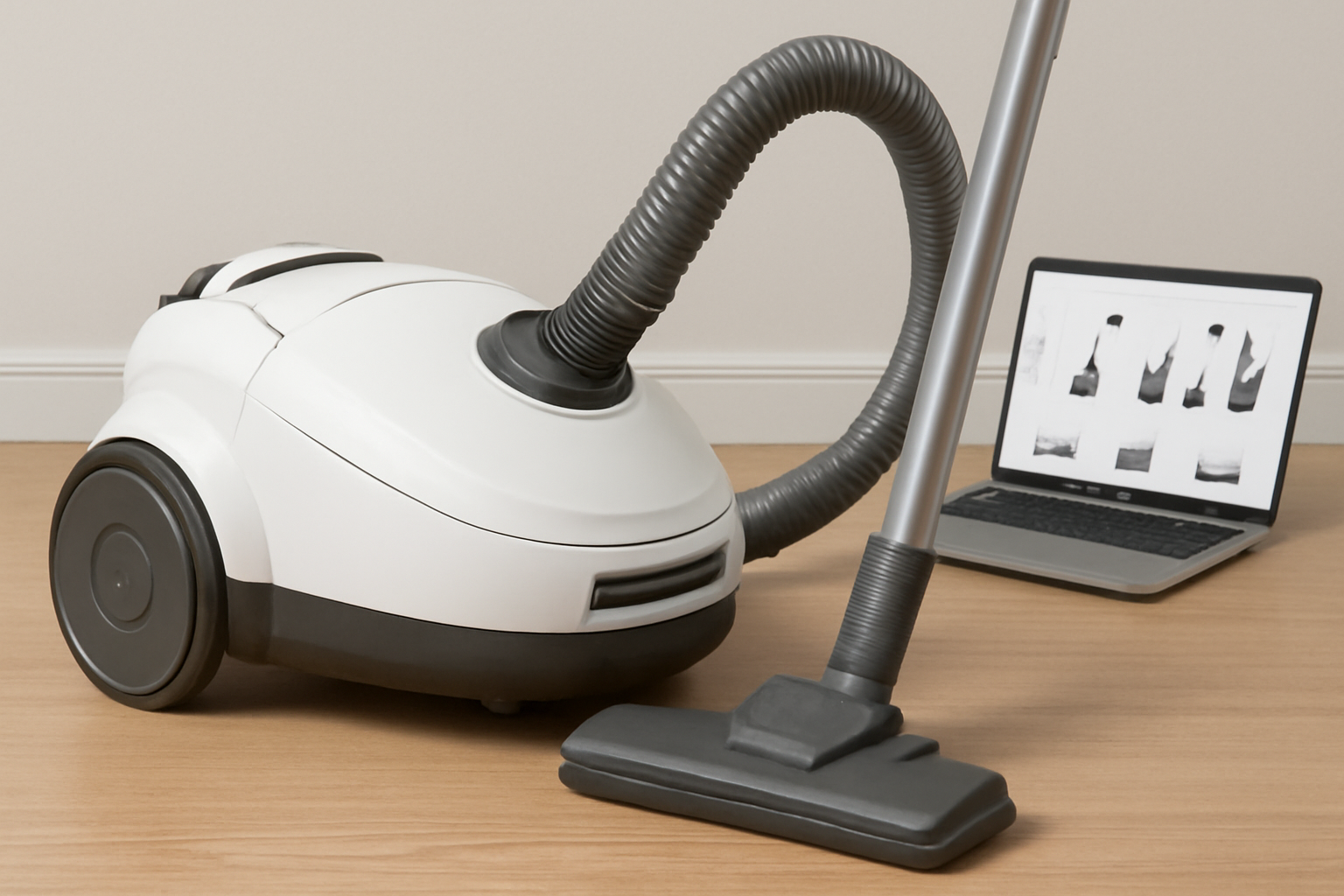
In Europe, digital transformation is redefining the appliance sector. Vacuum cleaner sales provide a clear illustration of how the shift to online commerce has changed buyer expectations, procurement methods, and brand competition. The post-2020 boom in home improvement, coupled with widespread digital literacy, accelerated adoption of e-commerce platforms. Both B2B and B2C buyers now view online channels not only as a marketplace but as a complete ecosystem that determines product visibility, logistics, and after-sales service.
This transition affects importers, distributors, and manufacturers equally. Understanding how platforms function—algorithmic ranking, data transparency, and fulfillment efficiency—has become as critical as understanding suction power or battery design. The result is a new hierarchy of market success, driven by information management rather than retail shelf space.
💻 1. The Structure of Europe’s Digital Marketplace
Europe’s e-commerce environment is unique: it integrates dozens of languages, currencies, and regulatory frameworks. Major general-purpose marketplaces such as Amazon EU, Allegro, and Cdiscount coexist with specialized platforms that target domestic buyers in France, Germany, or Scandinavia. National logistics networks are increasingly connected through EU-wide fulfillment systems, allowing even small producers to reach continental audiences within days.
For vacuum-cleaner suppliers, this means that competition happens simultaneously at local and regional levels. Importers use analytics dashboards to track pricing parity across multiple platforms, while algorithms determine exposure through conversion rates and review quality. Success therefore depends on data discipline: precise product information, accurate energy labels, and compliance documentation visible online.
🏭 2. Transformation in Procurement Behavior
Traditional bulk purchasing has evolved into data-driven sourcing. In modern vacuums procurement, decision-makers evaluate suppliers through digital performance indicators—delivery reliability, return statistics, and review averages—rather than long-term personal relationships alone.
Procurement specialists now operate through hybrid systems that integrate online wholesale portals with enterprise resource planning software. This combination allows automatic stock replenishment based on real-time sales data. For European importers, digital procurement reduces lead times and minimizes the financial risk associated with over-stocking physical warehouses.
At the same time, transparency forces suppliers to maintain consistent quality; negative reviews travel faster than any physical shipment. Reputation management, once a marketing task, has become a procurement concern.
⚙️ 3. Distribution Networks Re-imagined
The structure of vacuum cleaner distribution has changed more in five years than in the previous two decades. E-commerce encourages decentralization: goods move from central warehouses to regional micro-hubs that shorten delivery routes. Fulfillment-by-platform services—where the marketplace itself manages storage and shipping—allow small importers to compete with multinational brands.
Sustainability also influences distribution decisions. Many European retailers now calculate carbon intensity per shipment, rewarding suppliers who use recyclable packaging or participate in reverse-logistics recycling schemes. These environmental expectations align with broader EU targets for low-emission transport and waste reduction.
Digital tracking tools make this traceability measurable, converting logistics efficiency into a visible selling point.
📱 4. How Online Transparency Shapes Consumer Trust
European buyers, whether households or small businesses, rely heavily on user reviews, energy-efficiency labels, and verified-purchase ratings. The traditional salesperson’s role has largely migrated to digital interfaces that present comparable metrics: suction power, noise level, runtime, and filtration quality. Because data are public, competition becomes evidence-based.
For manufacturers, this transparency demands technical precision. Claims about cleaning efficiency must correspond to standardized tests recognized across EU markets. Many brands now publish downloadable test reports to substantiate performance figures. This data culture has elevated the technical literacy of consumers and narrowed the gap between engineering and marketing.
🧹 5. Product Diversification Through E-Commerce
Digital shelves have no physical limit, allowing retailers to list dozens of specialized models. As a result, European buyers encounter unprecedented diversity—from minimalist cordless sticks to industrial wet-dry units. Products like the Large-Capacity Wet Dry Vacuum Cleaner demonstrate how e-commerce expands visibility for professional-grade tools that might never appear in traditional retail stores.
At the same time, compact designs such as the Cordless Handheld Vacuum Cleaner appeal to urban consumers living in smaller spaces. Online comparison filters highlight weight, noise, and battery runtime, giving equal exposure to premium and budget categories. The long tail of product variety benefits both innovators and niche users.
🌐 6. Data Analytics and Predictive Demand
E-commerce provides unprecedented access to consumer data. Platforms track search frequency, abandoned carts, and review sentiment. For importers, these data streams become forecasting tools. They identify regional demand spikes—for example, allergy-season surges in HEPA-filter models—and allow factories to adjust production proactively.
This predictive capacity reduces waste and aligns manufacturing schedules with real consumption patterns. It also fosters collaboration between data analysts and product engineers, a relationship seldom seen in pre-digital supply chains.
🧭 7. Regulation and Compliance in the Digital Era
Selling across European borders involves navigating VAT harmonization, product-safety directives, and recycling obligations such as WEEE registration. Online platforms enforce these rules automatically, requiring documentation uploads before listing approval. The result is a form of self-regulation: compliance becomes the entry ticket to visibility.
Energy labeling remains central. The EU’s revised A-to-G scale forces manufacturers to optimize power consumption and disclose detailed metrics. Consumers can filter search results by energy grade, effectively rewarding eco-efficient design. The digital marketplace thus acts as an enforcement mechanism for sustainability standards.
📦 8. Logistics Innovation and Reverse Supply Chains
Fast delivery has turned logistics into a competitive differentiator. Companies experiment with urban micro-warehouses, drone delivery pilots, and shared transport corridors between major cities. For heavy or high-capacity models, hybrid shipping systems combine pallet freight with parcel last-mile networks.
Returns management—previously a cost center—now doubles as a sustainability indicator. Lower return rates signal higher quality and reduce emissions. Smart packaging that allows safe reshipment helps cut waste, aligning customer convenience with environmental goals.
💬 9. The Social Dimension: Reviews, Influencers, and Community Learning
E-commerce’s social layer shapes perception as much as technical features. Influencer demonstrations, short-form videos, and comparative testing dominate consumer research habits. Rather than reading long brochures, shoppers watch side-by-side demonstrations of suction power on multiple surfaces.
Manufacturers respond by creating educational content rather than advertisements, teaching users about filter maintenance or energy savings. In Europe’s multilingual context, subtitled tutorials reach cross-border audiences more efficiently than localized print campaigns. Trust now depends on authenticity and clarity rather than slogans.
🛒 10. Impact on Traditional Retail and Showrooms
Physical retailers adapt by integrating online tools—virtual catalogs, QR-linked specification sheets, and in-store pickup for online orders. Some specialize in after-sales services that e-commerce cannot fully replicate, such as repairs and consultations. The border between online and offline purchasing continues to blur; the dominant strategy is “omnichannel,” ensuring consistent pricing and warranty conditions regardless of where a purchase starts.
💡 11. The Role of Technology and Automation
Automation underpins every level of the online ecosystem. Artificial-intelligence algorithms predict which products deserve promotion, while robotic fulfillment centers handle packaging and dispatch. Machine-learning models optimize ad placement by analyzing millions of micro-interactions. For suppliers, participation requires structured product data and continuous optimization of listings to maintain visibility.
Manufacturers that integrate digital-twin simulations into production can synchronize inventory with online demand, reducing overstocks and markdowns.
🌿 12. Sustainability and Circular Economy
E-commerce both challenges and advances sustainability. The packaging footprint and delivery frequency increase emissions, yet digital traceability encourages greener behavior. Many European platforms now feature sustainability badges for products meeting recyclability and energy-efficiency criteria.
Buy-back and refurbishment programs close the product loop, enabling used devices to re-enter circulation through certified partners. These initiatives resonate strongly with younger consumers who value ecological accountability. Environmental transparency has become a measurable element of competitive advantage.
🔮 13. Future Outlook: AI Commerce and Hyper-Personalization
Artificial intelligence and augmented reality are shaping the next phase of digital purchasing. AR visualization lets users project a vacuum cleaner’s size in their living space before buying. AI chat assistants recommend models based on home size, floor type, and pet ownership. Predictive maintenance alerts, delivered through companion apps, transform one-time buyers into long-term service subscribers.
The convergence of smart-home technology with e-commerce platforms points toward a fully connected ecosystem where devices, users, and data continuously interact.
🌟 Conclusion
E-commerce has permanently changed the European vacuum-cleaner market. From procurement algorithms to consumer feedback loops, every stage of the supply chain now depends on digital infrastructure. Importers and distributors must master data analytics and compliance management as core competencies, while engineers design products with online visibility and logistical efficiency in mind.
The winners of this new landscape will be those who combine transparency, speed, and sustainability—turning digital information into long-term trust.
📌 Hashtags
#ECommerceTrends #DigitalProcurement #OnlineDistribution #SmartAppliances #CordlessVacuum #LargeCapacityVacuum #HomeApplianceMarket #SupplyChainInnovation #SustainableDesign #EnergyEfficiency #SmartHomeIntegration #ProductDataManagement #GreenRetail #CrossBorderTrade #VacuumCleanerIndustry #CustomerExperience #DataDrivenSales #ReverseLogistics #CircularEconomy #DigitalMarketing #PredictiveAnalytics #OmnichannelRetail #WarehouseAutomation #FastDelivery #OnlineReviewCulture #TransparencyInCommerce #VacuumsProcurement #VacuumCleanerDistribution #LargeCapacityWetDryVacuumCleaner #CordlessHandheldVacuumCleaner #HomeTechInsights #ConsumerBehavior #MarketForecast2025 #EcoLabelProducts #SmartFactory #RetailInnovation #FulfillmentCenter #AIinCommerce #AugmentedRealityRetail #HomeImprovementTrend #DigitalTransformation #EuropeECommerce #EcoFriendlyAppliances #ProductLifecycle #RecyclingPrograms #AfterSalesSupport #HomeCareTechnology #VacuumCleanerForAllergies #VacuumForMultiSurface #QuietVacuumForNightUse #CarVacuumCleaner #Lanxstar